1.Redis的介绍
Redis是一个开源(BSD许可),内存存储的数据结构服务器,可用作数据库,高速缓存和消息队列代理。它支持字符串、哈希表、列表、集合、有序集合,位图,hyperloglogs等数据类型。内置复制、Lua脚本、LRU收回、事务以及不同级别磁盘持久化功能,同时通过Redis Sentinel提供高可用,通过Redis Cluster提供自动分区。
中文文档:https://www.redis.net.cn/
2.入门
2.1 引入依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
<version>2.6.0</version>
</dependency>
|
2.2 添加配置类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
| package com.atguigu.yygh.common.config;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.time.Duration;
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public KeyGenerator keyGenerator() {
return new KeyGenerator() {
@Override
public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(target.getClass().getName());
sb.append(method.getName());
for (Object obj : params) {
sb.append(obj.toString());
}
return sb.toString();
}
};
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(600))
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(redisSerializer))
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer))
.disableCachingNullValues();
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = RedisCacheManager.builder(factory)
.cacheDefaults(config)
.build();
return cacheManager;
}
}
|
说明:
@EnableCaching:标记注解 @EnableCaching,开启缓存,并配置Redis缓存管理器。@EnableCaching 注释触发后置处理器, 检查每一个Spring bean 的 public 方法是否存在缓存注解。如果找到这样的一个注释, 自动创建一个代理拦截方法调用和处理相应的缓存行为。
2.3 配置文件中加入redis的配置
application.properties
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| spring.redis.host=localhost
spring.redis.port=6379
spring.redis.database= 0
spring.redis.timeout=1800000
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-active=20
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-wait=-1
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-idle=5
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.min-idle=0
|
2.4 使用Spring Cache + Redis执行缓存操作
2.1.2 @Cacheable
根据方法对其返回结果进行缓存,下次请求时,如果缓存存在,则直接读取缓存数据返回;如果缓存不存在,则执行方法,并把返回的结果存入缓存中。一般用在查询方法上。
| 属性/方法名 |
解释 |
| value |
缓存名,必填,它指定了你的缓存存放在哪块命名空间 |
| cacheNames |
与 value 差不多,二选一即可 |
| key |
可选属性,可以使用 SpEL 标签自定义缓存的key |
2.1.2 @CachePut
使用该注解标志的方法,每次都会执行,并将结果存入指定的缓存中。其他方法可以直接从响应的缓存中读取缓存数据,而不需要再去查询数据库。一般用在新增方法上。
| 属性/方法名 |
解释 |
| value |
缓存名,必填,它指定了你的缓存存放在哪块命名空间 |
| cacheNames |
与 value 差不多,二选一即可 |
| key |
可选属性,可以使用 SpEL 标签自定义缓存的key |
2.1.3 @CacheEvict
使用该注解标志的方法,会清空指定的缓存。一般用在更新或者删除方法上
| 属性/方法名 |
解释 |
| value |
缓存名,必填,它指定了你的缓存存放在哪块命名空间 |
| cacheNames |
与 value 差不多,二选一即可 |
| key |
可选属性,可以使用 SpEL 标签自定义缓存的key |
| allEntries |
是否清空所有缓存,默认为 false。如果指定为 true,则方法调用后将立即清空所有的缓存 |
| beforeInvocation |
是否在方法执行前就清空,默认为 false。如果指定为 true,则在方法执行前就会清空缓存 |
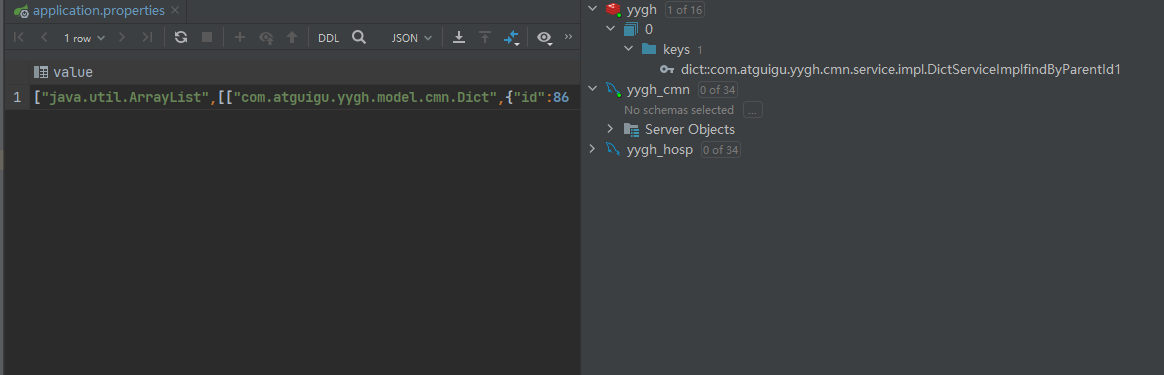
3.示例
下面的第一个方法是查询数据位list集合
@Cacheable(value = “dict”,keyGenerator = “keyGenerator”) 对方法的结果进行缓存
value属性表示key的前缀
keyGenerator表示key的生成规则,生成规则在配置文件中配置,这里我们使用的是方法的全类名作为key的后缀
第二个方法是添加数据 添加数据会造成数据库中数据的变化 我们要清除缓存
@CacheEvict(value = “dict”,allEntries = true) 清空指定的缓存
value属性表示清空以dict为前缀的所有缓存
allEntries 属性表示是否清空所有缓存,默认为 false。如果指定为 true,则方法调用后将立即清空所有的缓存
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| @Override
@Cacheable(value = "dict",keyGenerator = "keyGenerator")
public List<Dict> findByParentId(Long parentId) {
LambdaQueryWrapper<Dict> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(Dict::getParentId, parentId);
List<Dict> dictList = dictMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
for (Dict dict : dictList) {
dict.setHasChildren(this.isHasChildren(dict.getId()));
}
return dictList;
}
@CacheEvict(value = "dict",allEntries = true)
public void importDictData(MultipartFile file) {
try {
EasyExcel.read(file.getInputStream(),DictEeVo.class,new DictListener(dictMapper)).sheet().doRead();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
key的生成规则如下图: