一.需求分析
在审核文本内容的时候,我们可以调用第三方成熟的服务(例如阿里云的内容安全)来实现,但是基于不同的场景,第三方的服务不可能涉及到方方面面的敏感词,比如在游戏类的场景中,开挂一词算敏感词,但是在其它的场景中,开挂一词是一个正常的词汇。这时候需要我们根据不同场景自己维护一套敏感词,在文本审核的时候,需要验证文本中是否包含这些敏感词。
二.可选方案
| 方案 |
说明 |
| 数据库模糊查询 |
效率太低 |
| String.indexOf(“”)查找 |
数据库量大的话也是比较慢 |
| 全文检索 |
分词再匹配 |
| DFA算法 |
确定有穷自动机(一种数据结构) |
三. DFA算法
1.简介
DFA全称为:Deterministic Finite Automaton,即确定有穷自动机。
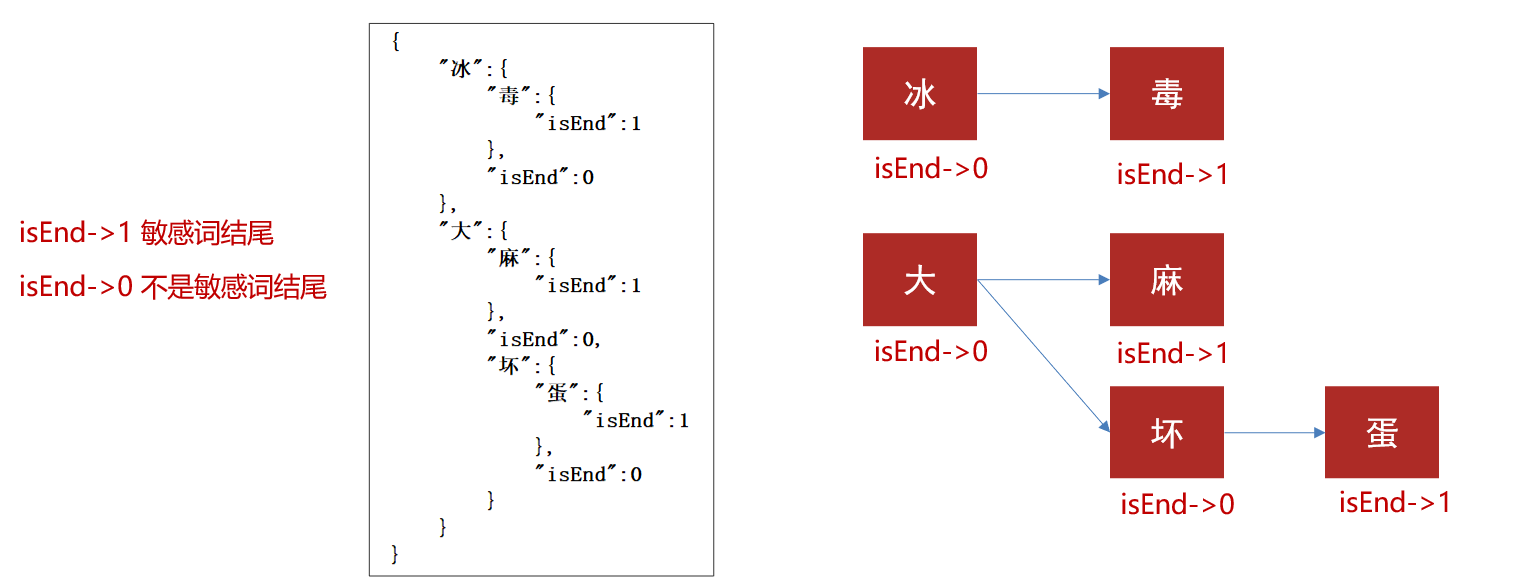
存储:一次性的把所有的敏感词存储到了多个map中,就是下图表示这种结构
敏感词:冰毒、大麻、大坏蛋
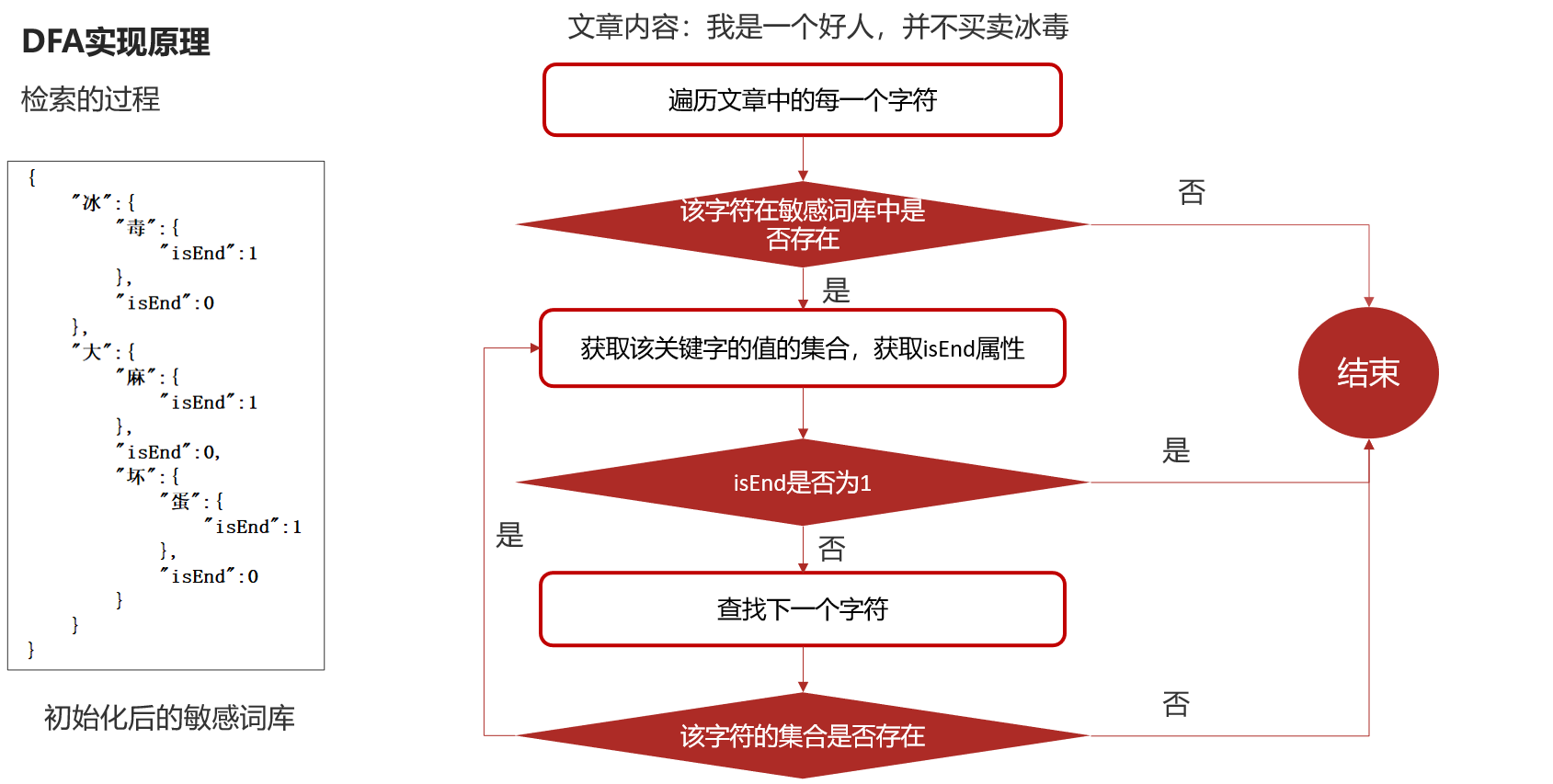
2.检索过程
四.工具类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
| package com.heima.utils.common;
import java.util.*;
public class SensitiveWordUtil {
public static Map<String, Object> dictionaryMap = new HashMap<>();
public static void initMap(Collection<String> words) {
if (words == null) {
System.out.println("敏感词列表不能为空");
return ;
}
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(words.size());
Map<String, Object> curMap = null;
Iterator<String> iterator = words.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
String word = iterator.next();
curMap = map;
int len = word.length();
for (int i =0; i < len; i++) {
String key = String.valueOf(word.charAt(i));
Map<String, Object> wordMap = (Map<String, Object>) curMap.get(key);
if (wordMap == null) {
wordMap = new HashMap<>(2);
wordMap.put("isEnd", "0");
curMap.put(key, wordMap);
}
curMap = wordMap;
if (i == len -1) {
curMap.put("isEnd", "1");
}
}
}
dictionaryMap = map;
}
private static int checkWord(String text, int beginIndex) {
if (dictionaryMap == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("字典不能为空");
}
boolean isEnd = false;
int wordLength = 0;
Map<String, Object> curMap = dictionaryMap;
int len = text.length();
for (int i = beginIndex; i < len; i++) {
String key = String.valueOf(text.charAt(i));
curMap = (Map<String, Object>) curMap.get(key);
if (curMap == null) {
break;
} else {
wordLength ++;
if ("1".equals(curMap.get("isEnd"))) {
isEnd = true;
}
}
}
if (!isEnd) {
wordLength = 0;
}
return wordLength;
}
public static Map<String, Integer> matchWords(String text) {
Map<String, Integer> wordMap = new HashMap<>();
int len = text.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
int wordLength = checkWord(text, i);
if (wordLength > 0) {
String word = text.substring(i, i + wordLength);
if (wordMap.containsKey(word)) {
wordMap.put(word, wordMap.get(word) + 1);
} else {
wordMap.put(word, 1);
}
i += wordLength - 1;
}
}
return wordMap;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("法轮");
list.add("法轮功");
list.add("冰毒");
initMap(list);
String content="我是一个好人,并不会卖冰毒,也不操练法轮功,我真的不卖冰毒";
Map<String, Integer> map = matchWords(content);
System.out.println(map);
}
}
|
结果:
最佳实践: 项目实战-黑马头条 | The Blog (qingling.icu)








